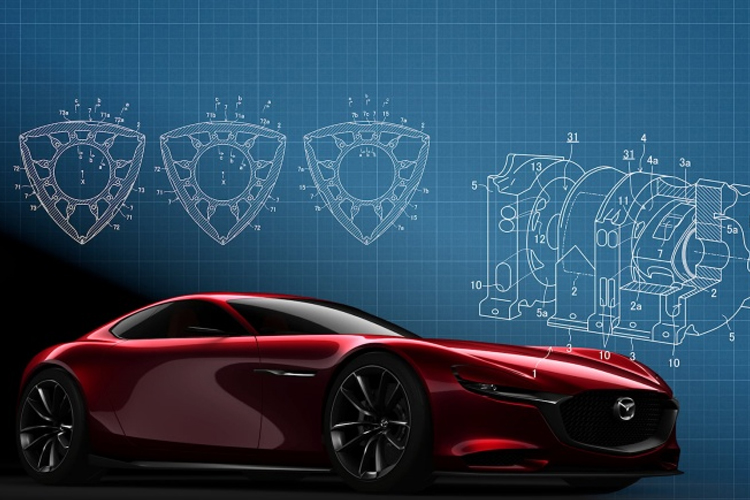
Mazda Motor Corporation is revolutionizing the automotive industry with the development of advanced 3-rotor rotary engines. Unlike the traditional 1-rotor design used in the Mazda MX-30 e-SkyActive R-EV plug-in hybrid, the 3-rotor design offers enhanced practicality and performance.
According to a recent CarBuzz report, Mazda has filed 6 patent applications, with 3 of them (Patent 1, Patent 2, and Patent 3) focusing on the intricate design of the rotor itself. These patents aim to optimize the fuel efficiency of rotary engines, marking a significant step forward for Mazda’s innovation in the field.
Each patent delves into the detailed design of the rotor surface, employing unique indentations that vary in length, width, and depth. These indentations play a crucial role in shaping the combustion chamber, where the air-fuel mixture is ignited by a spark plug and powers the engine.
Mazda’s patent files elaborate on how the geometry of the combustion chamber influences ignition timing and the expansion of flames during combustion. By carefully manipulating the chamber’s geometry, Mazda can expedite or delay ignition, thereby enhancing the thermal efficiency of the rotary engine.
This innovative combustion chamber design not only accelerates the combustion process and ensures complete combustion of the air-gasoline mixture before reaching the exhaust port but also effectively mitigates heat and exhaust gas emissions resulting from incomplete combustion.
Also Read: Chinese Cars Set to Dominate 15% of the Entire European Electric Car Market
To address previous design flaws in rotary engines, Mazda has incorporated curved surfaces into the combustion chamber. This curvature causes the chamber to gradually narrow as it approaches Top Dead Center during the ignition stroke.
The advantage of this design approach is that it facilitates the maintenance of the proper air-fuel ratio, allowing for leaner combustion and reducing gas leakage—an issue commonly associated with rotary engines.
Furthermore, Mazda has introduced wider indentations on the rotor design, with deeper indentations towards the center of the rotor, while adjusting the surface indentation on the engine block to a shallower depth. This meticulous configuration optimizes the flow of the air-fuel mixture and contributes to improved performance and efficiency.
In conclusion, Mazda’s ongoing development of 3-rotor engine models signifies a significant breakthrough in the automotive industry. By prioritizing fuel efficiency and employing intricate rotor design, Mazda is set to redefine the capabilities of electric cars. The innovative geometry of the combustion chamber and the incorporation of curved surfaces address past challenges and promise improved combustion efficiency and reduced emissions. As Mazda continues to push the boundaries of rotary engine technology, we can anticipate a new era of high-performance electric vehicles on the horizon.